Mink Frog
North American Green Frog, Swamp Frog
Lithobates septentrionalis
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
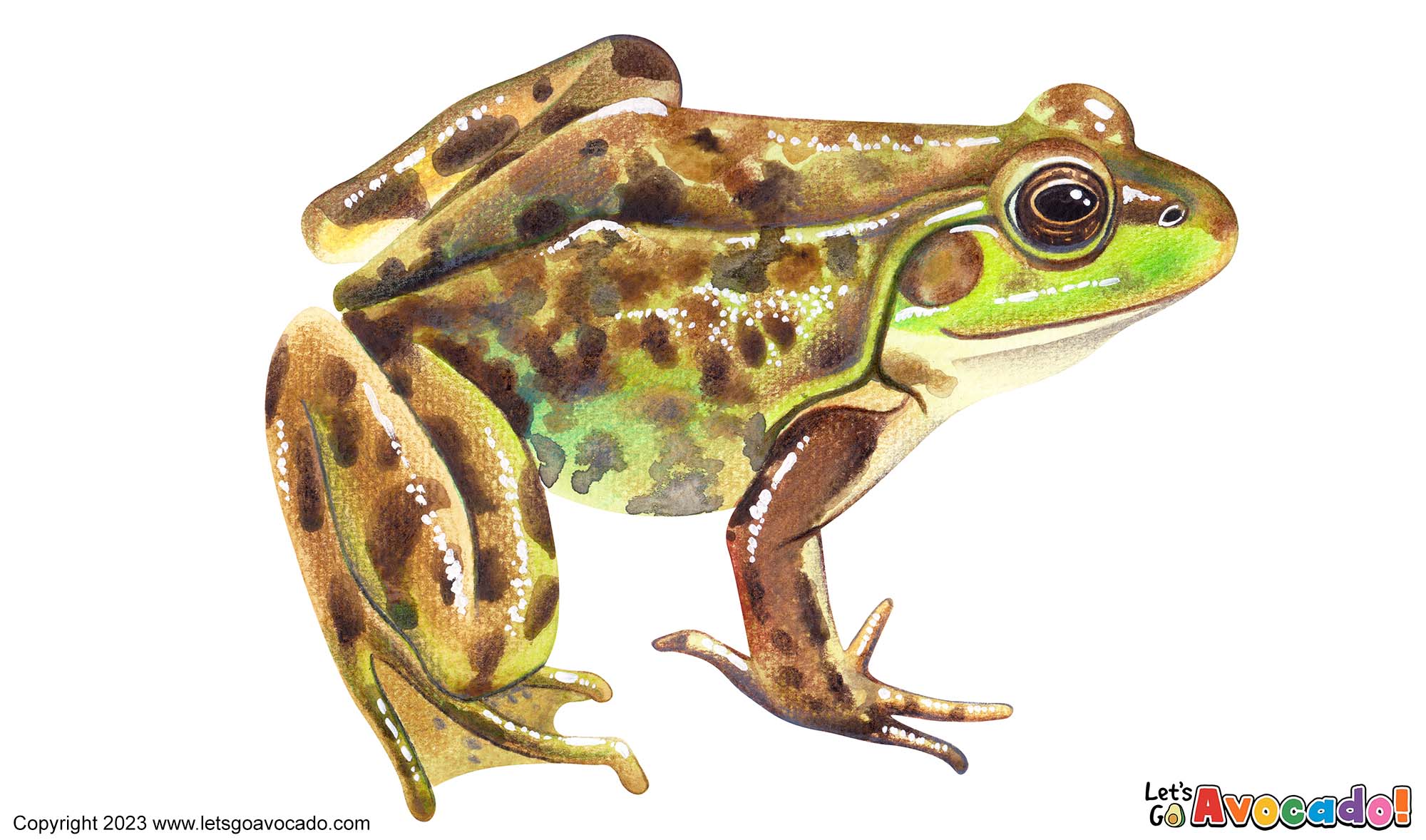
The Mink Frog, scientifically known as Lithobates septentrionalis, is a fascinating amphibian species found in North America. These frogs are named after their resemblance to the fur of the mink, with their mottled brown or olive-green skin coloration and dark markings. They are medium-sized frogs, ranging from 2.5 to 3.5 inches (6 to 9 centimeters) in length. Mink Frogs inhabit wetland areas such as marshes, ponds, and lakes, particularly those with abundant vegetation. They are well adapted to an aquatic lifestyle and are excellent swimmers. These frogs are known for their distinct vocalizations, which sound like a series of loud, deep snoring or chuckling sounds. Mink Frogs have a diverse diet, feeding on insects, spiders, small fish, tadpoles, and even other frogs. Their lifecycle includes laying eggs in shallow water, with the tadpoles hatching and undergoing metamorphosis into adult frogs. While Mink Frogs are not of significant conservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Learn More concern, their presence in wetland ecosystemsAn ecosystem is a community of living organisms, like insects and birds, and non-living components, like water and rocks, that interact with each other in a specific area. Learn More contributes to the overall biodiversityBiodiversity refers to the variety of living things in an ecosystem. The more biodiversity there is in an ecosystem, the healthier and stronger it is. Learn More and functioning of these habitats.
Mink Frog
Common Name
Other Names
Latin Name
Distribution
Appearance
Size
Habitat
Behavior
Diet
Lifecycle
Vocalization
Defense Mechanisms
Ecological Importance
Conservation Status

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.