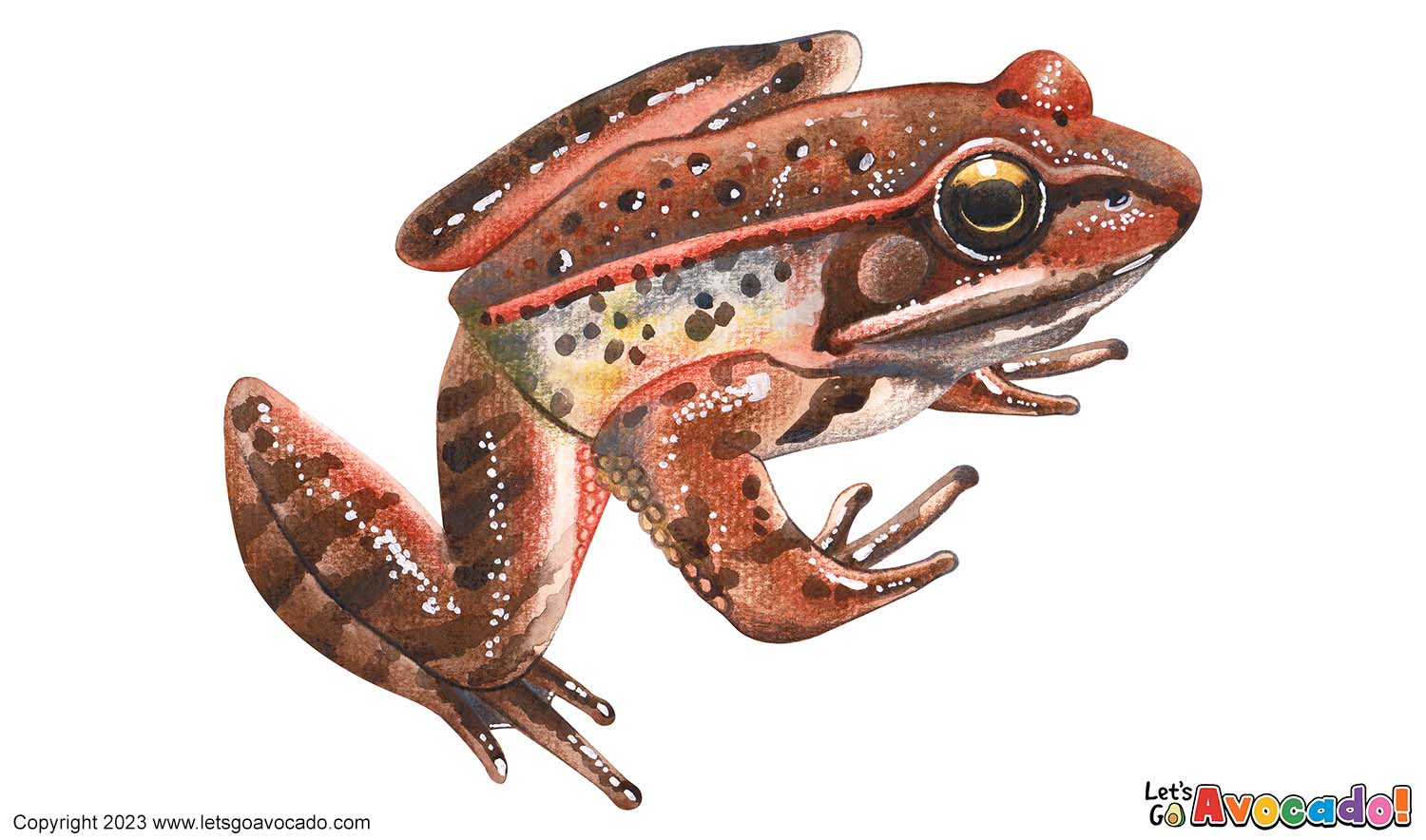
Northern Red-Legged Frog
The Northern Red-Legged Frog is also known as the Aurora Frog or Rana aurora.
Rana aurora
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
The Northern Red-Legged Frog, also known as Rana aurora, is a fascinating amphibian species native to the Pacific Northwest region of North America. These frogs get their name from the reddish coloration found on the undersides of their legs. They have a smooth and moist skin that varies in color from brown to green, often adorned with dark blotches or speckles, providing excellent camouflage in their natural habitat. These medium-sized frogs typically measure around 2.5 to 3.5 inches (6 to 9 centimeters) in length. They inhabit a range of wetland habitats, including ponds, marshes, and forested areas near water bodies. Northern Red-Legged Frogs are highly adapted to an aquatic lifestyle, spending most of their time in or near water. They are skilled swimmers and have long hind legs for powerful jumping. These frogs are known for their distinctive vocalizations, producing a series of low-pitched, raspy croaks during the breeding season. They have a diverse diet, feeding on a variety of invertebrates, including insects, spiders, and small crustaceans. The lifecycle of Northern Red-Legged Frogs follows the typical pattern of amphibians, with breeding taking place in spring and early summer. Females lay their gelatinous egg masses in shallow water, and the eggs hatch into tadpoles. These tadpoles undergo metamorphosis, gradually developing legs and lungs until they transform into fully-formed adult frogs. The conservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Learn More status of Northern Red-Legged Frogs is of concern, as their populations have declined due to habitat loss, pollution, and the introduction of non-native species. Efforts are underway to protect their habitats and ensure their survival in the wild. These frogs play an essential role in their ecosystemsAn ecosystem is a community of living organisms, like insects and birds, and non-living components, like water and rocks, that interact with each other in a specific area. Learn More, serving as both predators and prey and contributing to the overall biodiversityBiodiversity refers to the variety of living things in an ecosystem. The more biodiversity there is in an ecosystem, the healthier and stronger it is. Learn More of their habitats.
Northern Red-Legged Frog
Common Name
Other Names
Latin Name
Distribution
Appearance
Size
Habitat
Behavior
Diet
Lifecycle
Vocalization
Defense Mechanisms
Ecological Importance
Conservation Status

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.