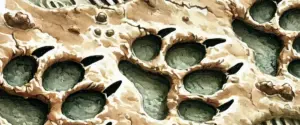
Bird’s Nest Fungi
Splash cups
Genera Nidula, Crucibulum, Cyathus, and Mycocalia
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
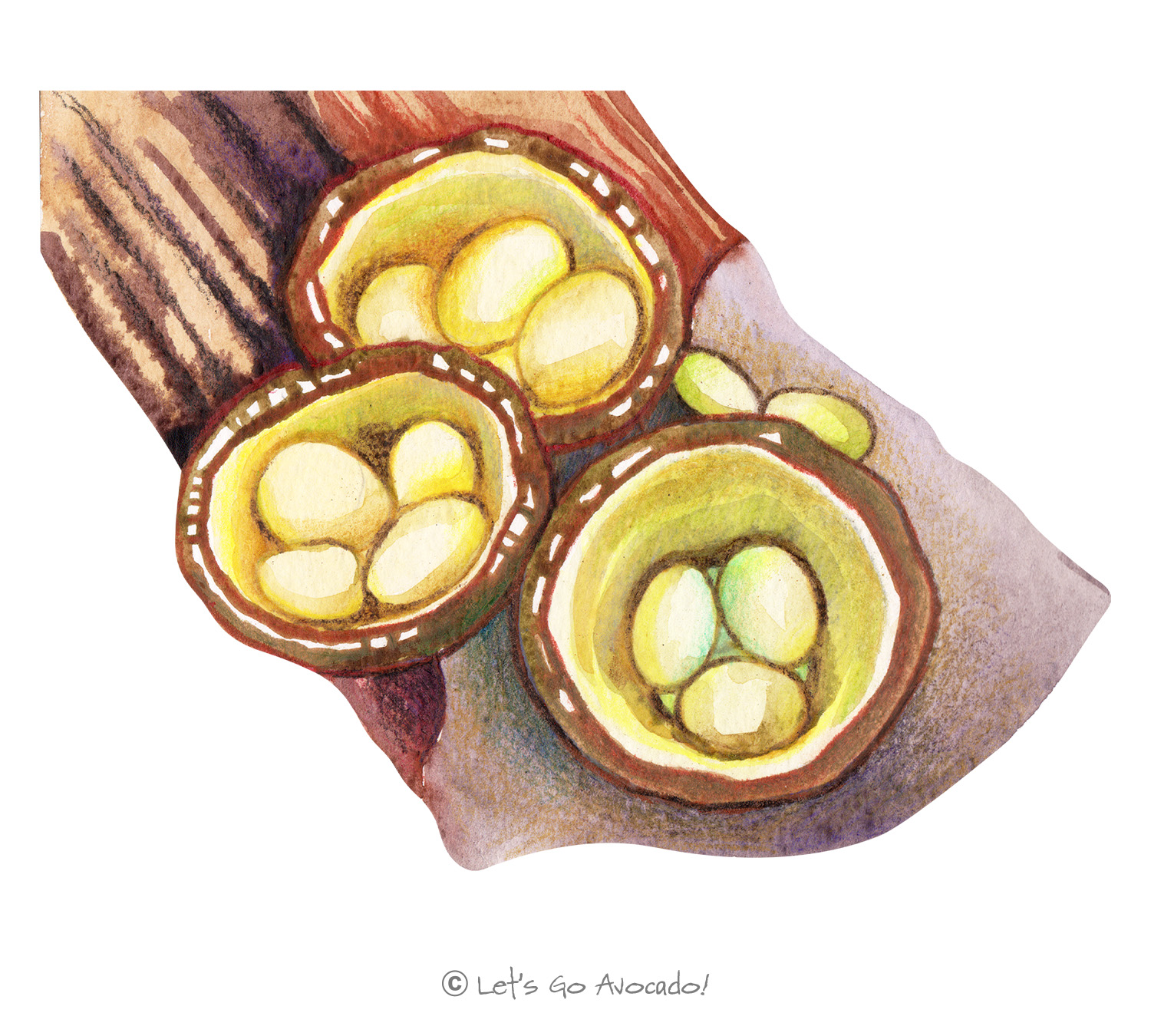
Bird’s Nest Fungi are unique and fascinating fungi known for their nest-like appearance, containing small egg-like structures called peridioles. These “eggs” are actually capsules containing spores.
Bird’s Nest Fungi
Common Name
Other Names
Latin Name
Distribution
Appearance
Size
Habitat
Diet
Lifecycle
Defense Mechanisms
Ecological Importance
ConservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Learn More Status

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.