Straight Branched Coral
Coral mushroom
Ramaria sp.
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
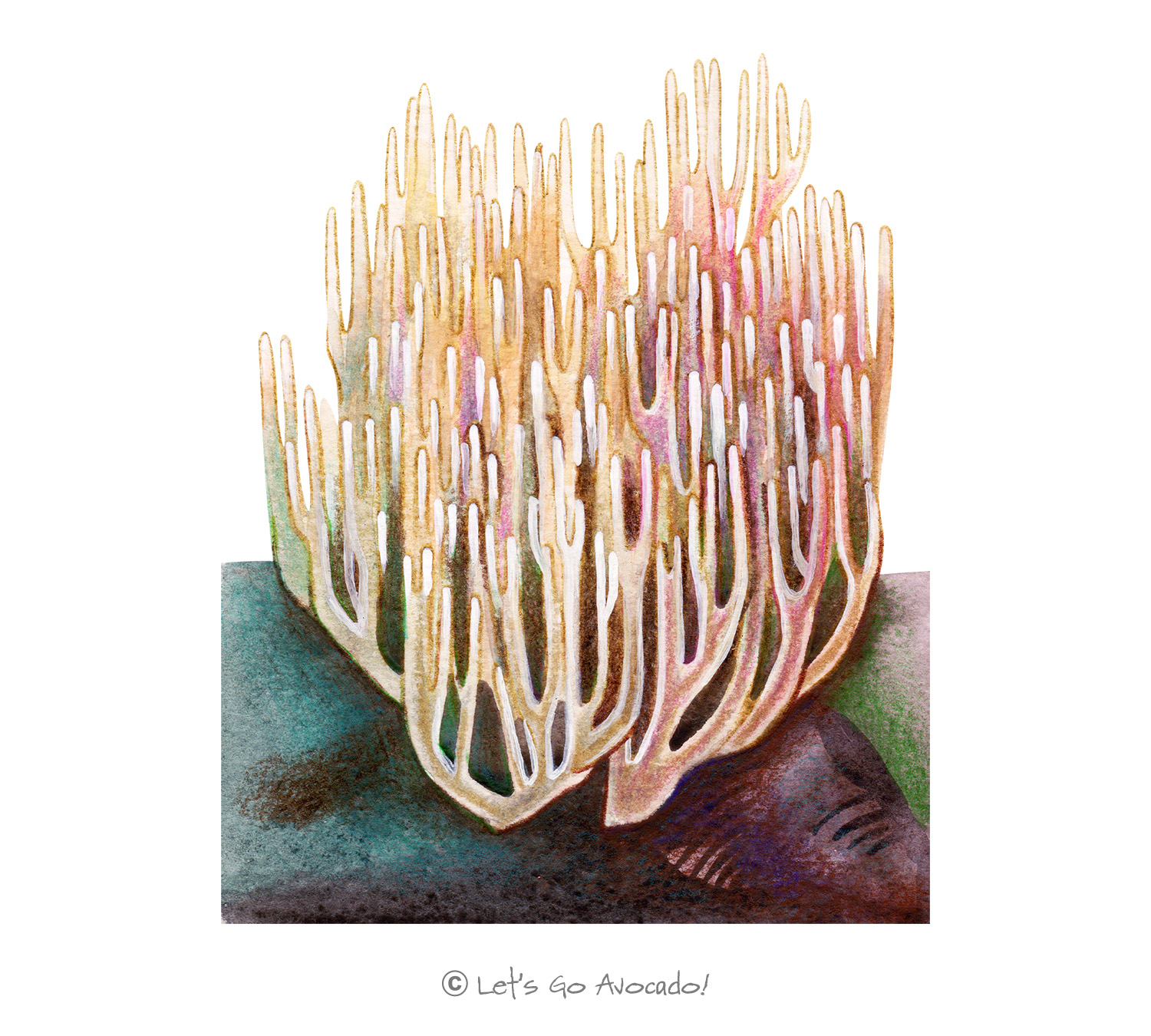
The Straight Branched Coral mushroom, as its name suggests, resembles underwater coral formations. This terrestrial fungi belongs to a larger group of mushrooms known for their intricate, branched structures which can be a delight to come across in the forest.
Straight Branched Coral
Common Name
Straight Branched Coral
Other Names
Coral mushroom
Latin Name
Ramaria sp.
Distribution
This mushroom is primarily found in North America and Europe.
Appearance
Straight Branched Coral mushrooms have tall, straight branches that can be densely packed. They can vary in color but are commonly yellowish, tan, or pale brown. The tips can sometimes be a different color, often a bit darker.
Size
They typically grow to be about 8 to 20 cm tall.
Habitat
Coral fungi, including the Straight Branched Coral, are typically found on the ground in forests, especially under conifer trees.
Diet
These fungi are saprobic, meaning they feed on decaying organic matter, often helping to decompose fallen wood and forest litter.
Lifecycle
Like other fungi, the Straight Branched Coral mushroom reproduces via spores. These spores are released from the tips of the branches and spread by wind or water. Once they land in a favorable environment, they germinate and, given the right conditions, will grow into a new mushroom.
Defense Mechanisms
The exact defense mechanisms for the Straight Branched Coral mushroom aren’t well-documented, but many fungi contain compounds that deter herbivores or have unpalatable textures.
Ecological Importance
As saprobic fungi, they play a crucial role in breaking down and recycling organic matter in forests. This process helps in returning nutrients to the soil, supporting the forest ecosystem’s health.
Conservation Status
It’s generally considered common where it’s found.

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.