The Sugar Maple Tree: Nature’s Sweet Gift
Ever wonder where delicious maple syrup comes from? Say hello to the Sugar Maple tree, officially known as Acer saccharum! This tree is a superstar in the forest, especially famous in the northeastern United States and Canada. The Sugar Maple isn’t just about sweet syrup; it’s also a dazzling part of the forest, especially in the fall when its leaves turn into a firework display of colors.
Spotting a Sugar Maple
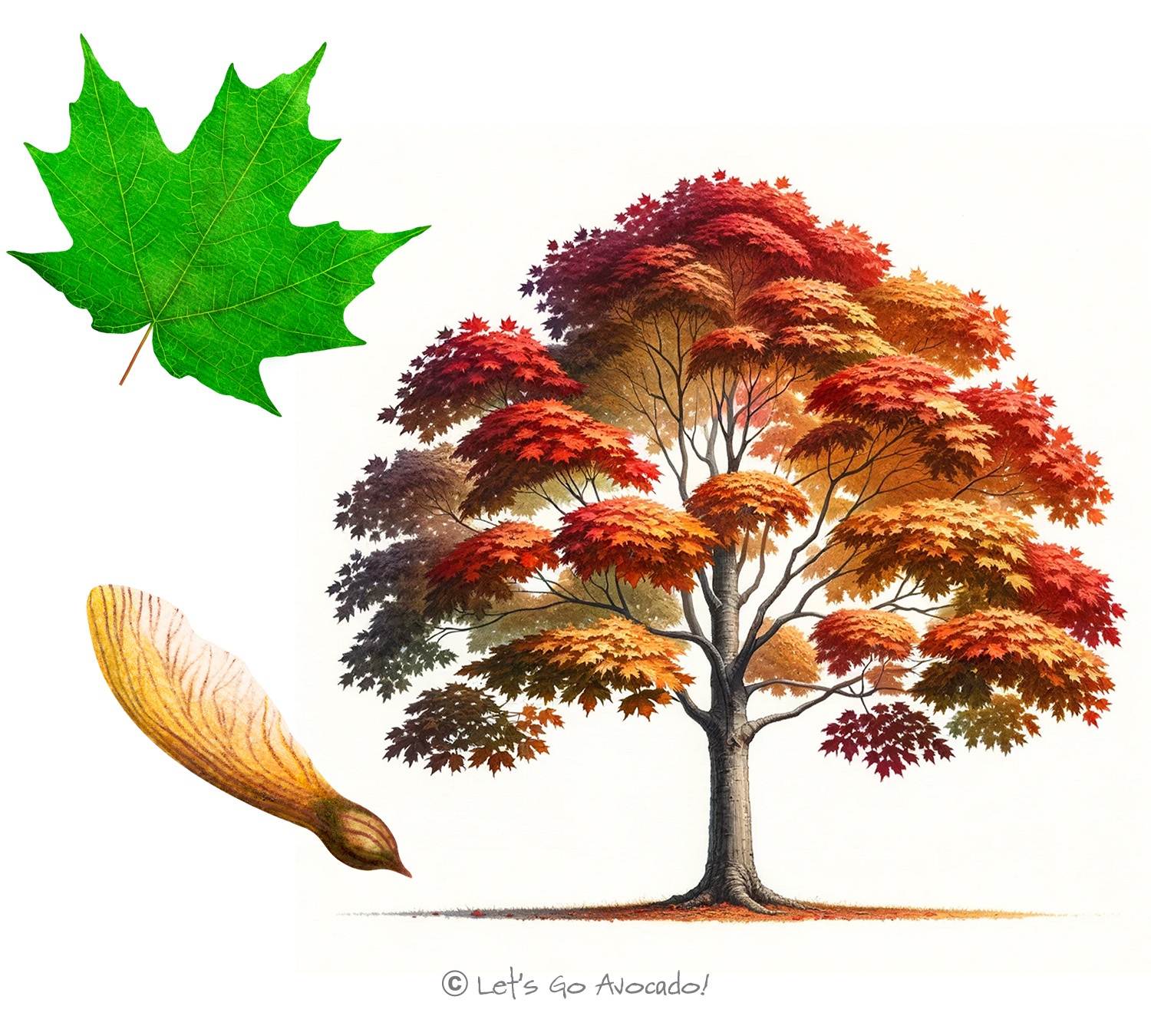
The Sugar Maple is easy to identify with its star-shaped leaves that have five points. These leaves are summer-green and transform into brilliant shades of yellow, orange, and red in the fall. It’s like a natural light show! The tree also has smooth, gray bark when it’s young, which becomes more rugged and groovy as it gets older.
How Big and Tall Does It Grow?
Sugar Maples are pretty big trees, growing up to 60-75 feet tall – that’s like stacking about 12 elephants on top of each other! They can also spread wide, making a big, leafy umbrella in the forest or your backyard. This tree is the perfect shade-maker for sunny days.
The Life of a Sugar Maple
In springtime, the Sugar Maple wakes up and grows small, delicate flowers. Then, it produces winged seeds that twirl down to the ground like tiny helicopters. These seeds might grow into new trees! But the coolest part? In late winter and early spring, people tap the trees to collect sap, which is boiled down to make maple syrup – yum!
Why the Sugar Maple Is Important
The Sugar Maple does a lot for the environment. It cleans the air, provides homes for birds and squirrels, and its leaves add nutrients to the soil when they fall. It’s also a big deal for wildlife, providing food and shelter. And let’s not forget about the maple syrup and beautiful fall colors it gives us!
Is the Sugar Maple a Tough Tree?
Yep, the Sugar Maple is pretty tough. It likes cold climates and can handle some rough winters. It’s strong and healthy but needs enough water and good soil to grow big and make lots of syrup.
People and the Sugar Maple
People love Sugar Maples for their syrup, of course, but also for their wood, which is used to make furniture and even musical instruments. And because of their beautiful fall colors, these trees are popular in parks and big yards.
The Sugar Maple tree is a sweet part of nature, literally! It gives us tasty syrup and brightens up our autumns with amazing colors. It’s not just a tree; it’s a part of our seasons and celebrations, especially when the leaves start to change. Next time you enjoy some maple syrup, think of the Sugar Maple trees and all the cool things they do for us and the environment.
Every tree in the forest has its own special thing, just like the Sugar Maple with its yummy syrup and colorful leaves. Keep exploring and learning about trees, and you’ll see how each one adds something special to our world!